Educational
Biosphere VR in education
Educational
Biosphere VR in education
A quick look at the VR travel used in a school setting. (Subtitles is available by hitting the icon under the video)
Now it’s your turn to act - Take the JOURNEY INTO THE BIOSPHERE and learn on your way.
Frontpage of the 100 page educational guide manual that takes the user through landscapes of STEM and exploration.
In Biosphere VR, we invite you to embark on a critical and creative journey to find answers and solutions to the pressing climate issues we face today. Through our immersive virtual reality experiences set in Jordan, Kiribati, Beijing, China, Ethiopia, Morocco, or Sweden, you will witness the challenges firsthand.
Our objective is to provide a transformative experience through virtual reality, followed by engaging group dialogues. Together, you'll develop innovative concepts to address the problems you witnessed. When a shared understanding of the problem and solution emerged, it was presented to the larger group.
During our testing phase in Hellerup, Denmark, we received valuable feedback from participants. The results were overwhelmingly positive.
“94 % answered that they would like initiatives like Biosphere VR to be more significant in school.”
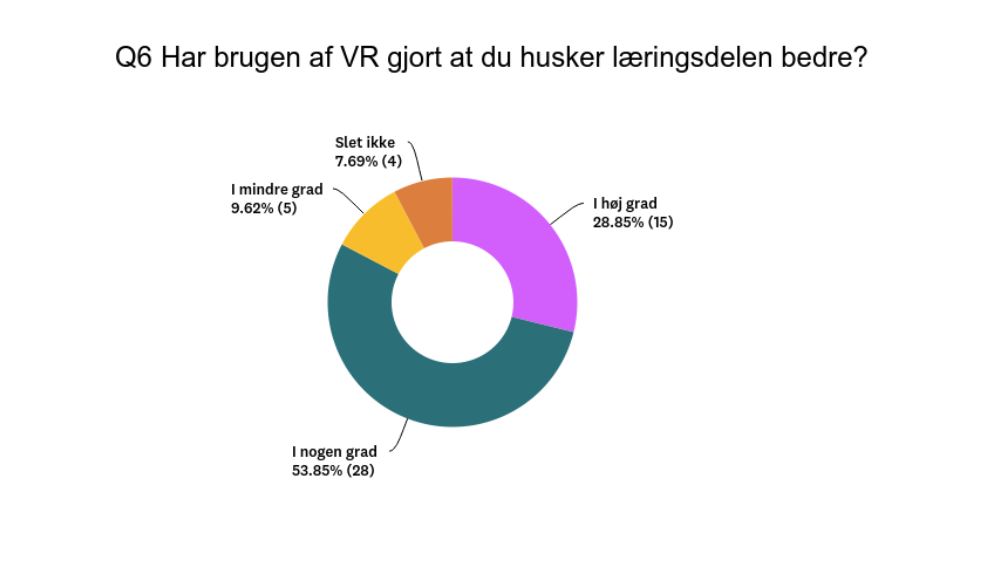
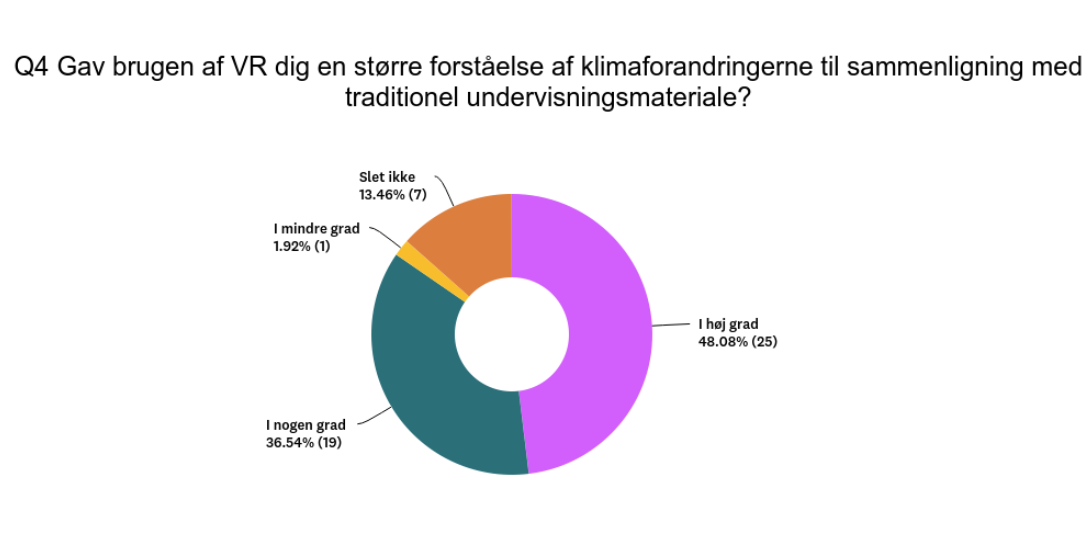
“83 % said that they remembered the subject better using Biosphere VR compared with traditional teaching materials.”
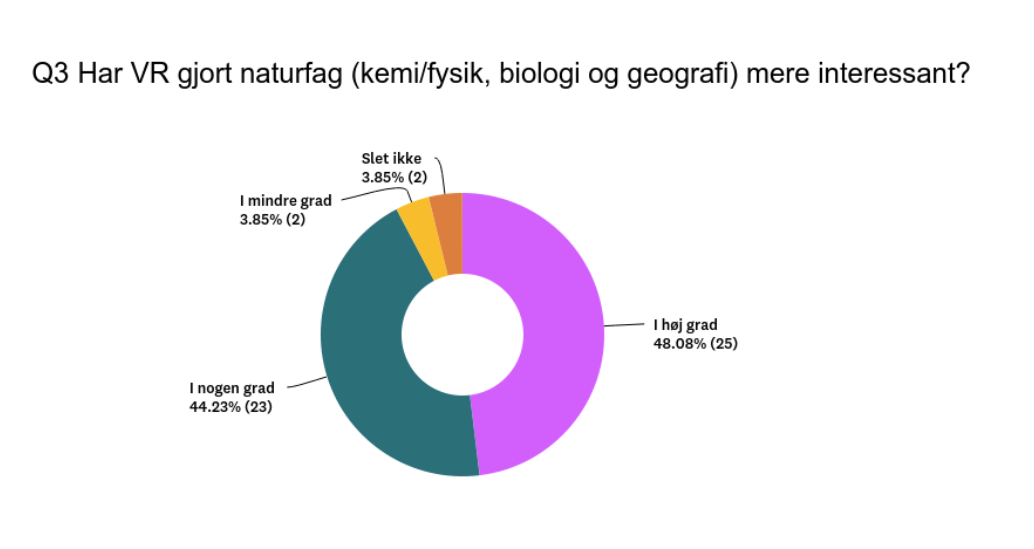
“92% answered that Biosphere VR made learning STEM subjects more interesting.”
School teacher Larry. Click below video for subtitle
““I think that VR, in this case, makes the journey out to the affected countries very real and leaves a strong impression on us - a lesson for life”
We surveyed at the progressive Maglegårds School in Hellerup, Denmark, to gather data on the impact of Biosphere VR. Out of the 60 questionnaires distributed digitally, we received 52 completed responses, representing an 86.6% response rate. The study included 39.22% girls (20) and 60.78% boys (31).
A test at the progressive Maglegårds school, Hellerup 2019
The results provide valuable insights into the benefits and outcomes of using VR in educational settings. Here are the key findings from our research:
Increased Interest in Science: A significant majority of students expressed a heightened interest in science due to the use of VR. Out of all respondents, 48% reported that VR had significantly made science more interesting, while 44% stated it had to some extent. Only 8% believed it had lesser or no impact on their interest in science.
Gender Differences: The survey revealed notable gender differences regarding the impact of VR on interest and understanding. Among girls, 95% reported that VR had to some degree made science more interesting, while the response from boys stood at 90%. Similarly, 70% of girls felt that VR facilitated a greater understanding of climate change compared to traditional teaching materials, while the corresponding figure for boys was 35%. However, 45% of boys agreed to some extent, compared to 20% of girls. Overall, 15% of respondents believed the impact to be lesser or not at all.
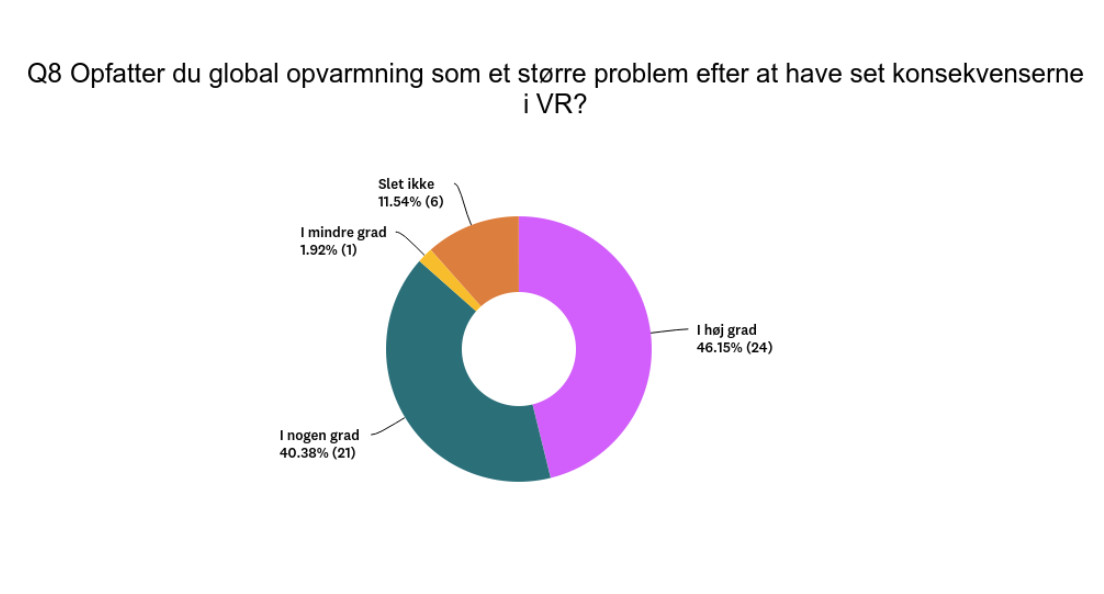
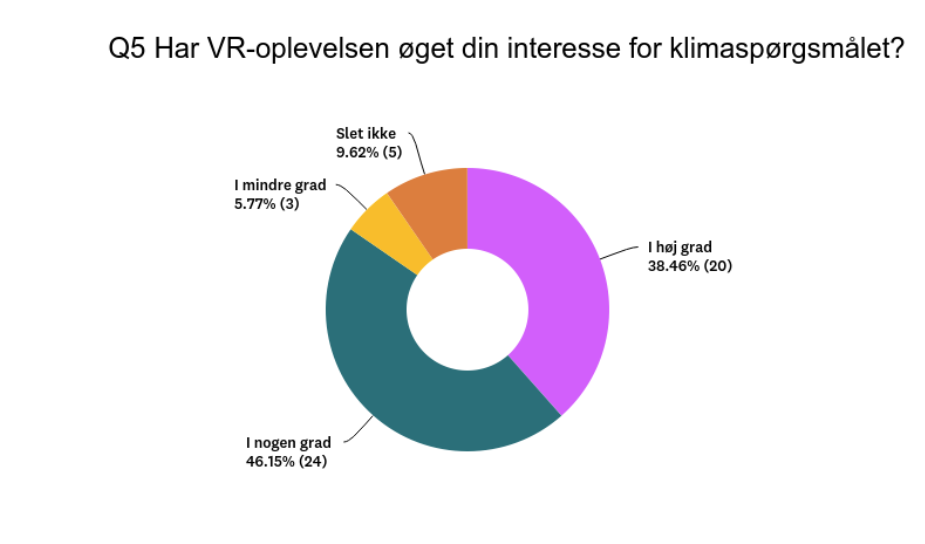
Increased Interest in Climate: The survey demonstrated that the VR experience significantly or to some extent increased students' interest in the climate. A substantial 85% of students reported a greater interest in the climate after experiencing VR, and 87% perceived global warming as a major problem after witnessing its consequences in VR. The gender disparity was evident, with 95% of girls and 81% of boys reporting increased interest in the climate.
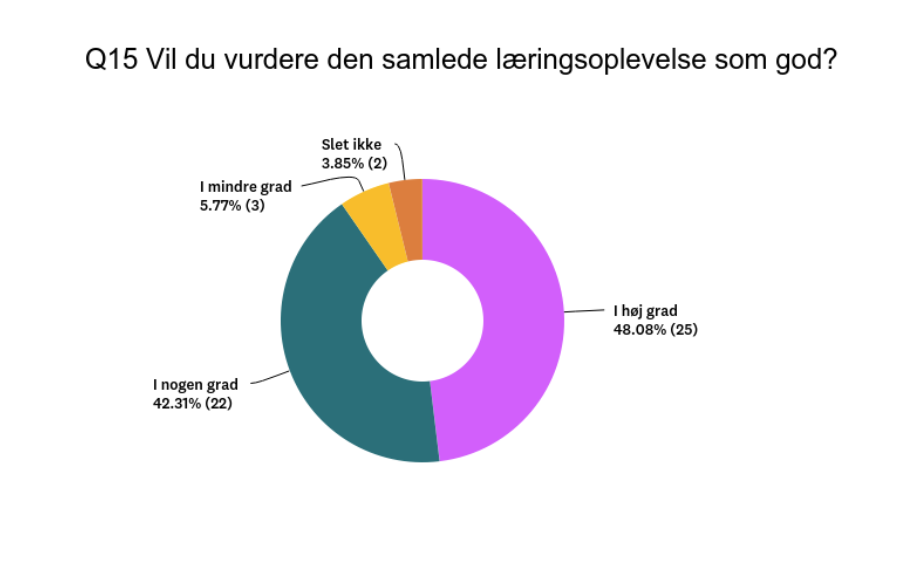
Improved Learning Outcomes: The findings strongly support the notion that VR positively affects learning outcomes. Around 83% of students agreed that VR helped them remember what they learned to a high or some extent. Additionally, 90% believed that incorporating VR into their project work made sense. Moreover, 94% expressed a desire for increased integration of VR into their education. Notably, a higher proportion of girls (90%) reported improved learning retention compared to boys (76.7%).
VR Experience: The majority of respondents (75%) had prior experience with VR, mainly through entertainment applications such as theme park rides or gaming consoles. However, none of the participants had previous educational experience with VR. Among girls, 74% reported high or some experience, while the figure was 75% for boys. Additionally, 20% of girls stated no prior experience with VR.
Our VR Learning Platform: Biosphere VR (www.biospherevr.com)
“85% said that Biosphere VR significantly, or to some degree, heightened their interest in the effects of the climate”
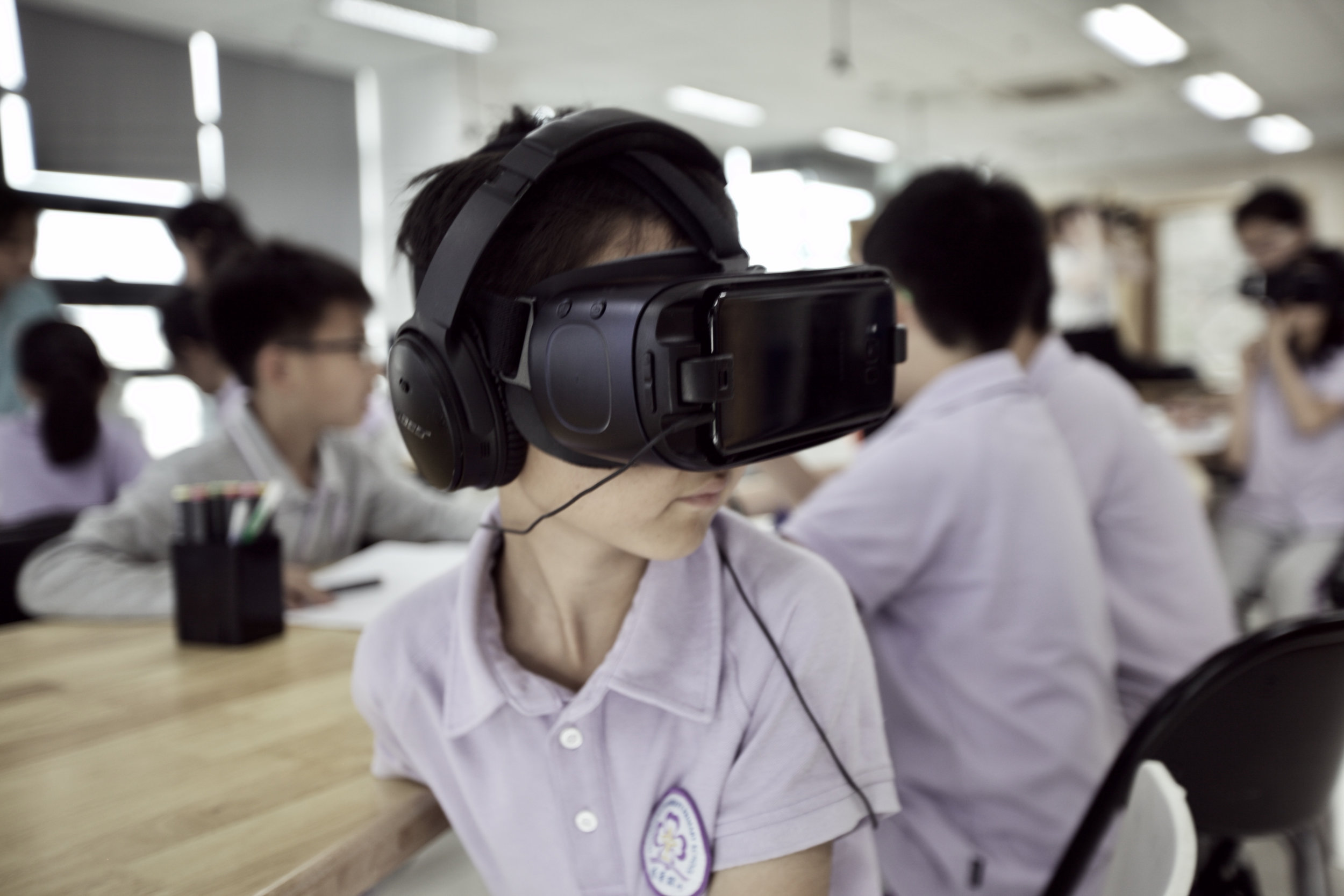
A succesfull test conducted at The Learning Lab, Tsinghus University, Beijing 2018
The data behind
The Danish Film Institute financed a survey and a subsequent presentation of the findings regarding the utilization of Biosphere VR within an educational setting. This study was conducted at Maglegrd School in Hellerup, Denmark, involving 70 students from classes 7-9. The survey was administered in Danish, and the responses were represented by specific colors. In the survey, the color purple denoted a strong inclination or support, the petroleum color indicated a general favorability, the yellow color represented a slight agreement, and the orange color indicated a complete lack of agreement.